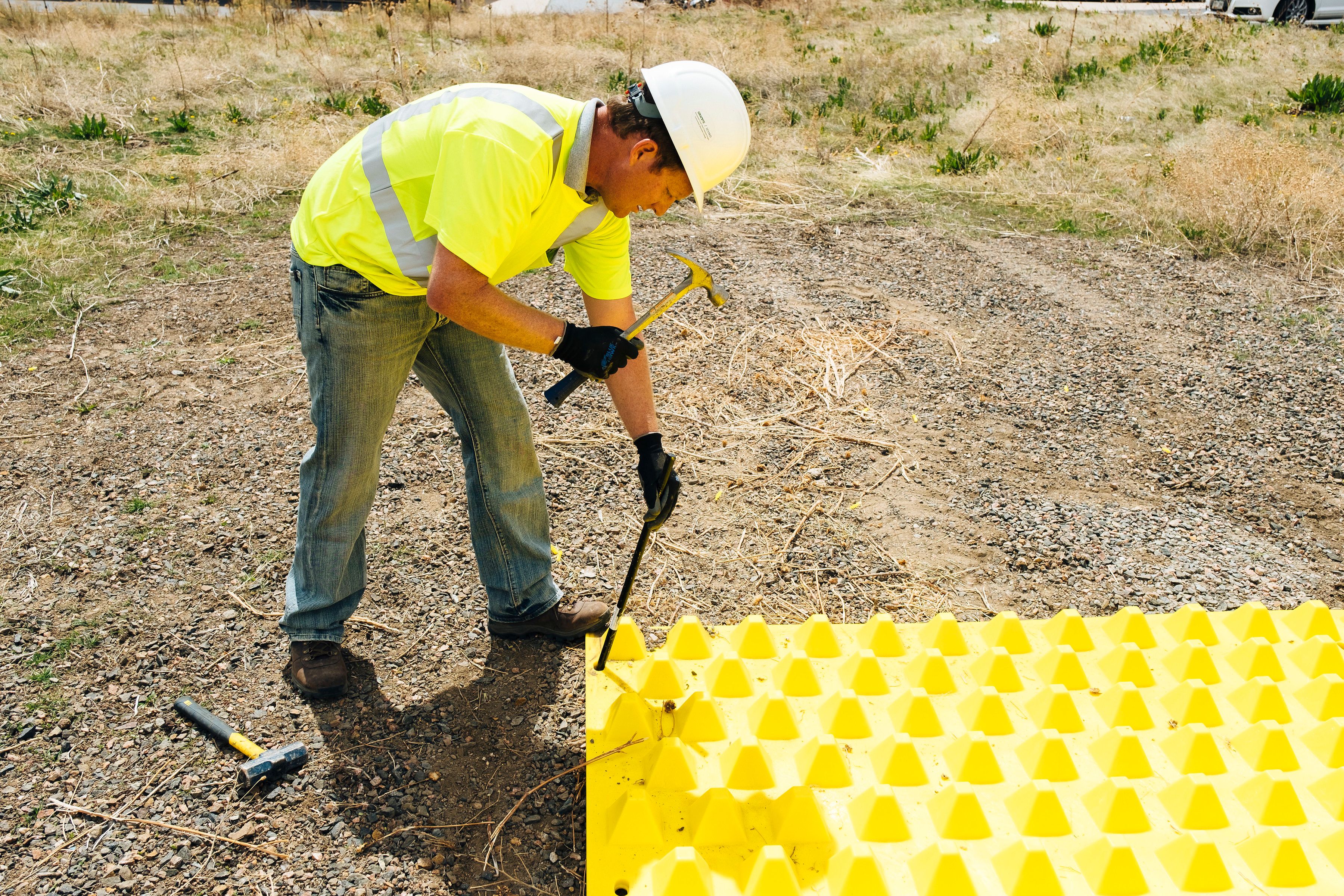
4 Easy Steps To Install
Choose the right construction entrance configuration for your project that aligns with your SWPPP guideline. Contact us or call us at (844) 200-3637 for recommendations.
Locate underground utilities before anchoring.
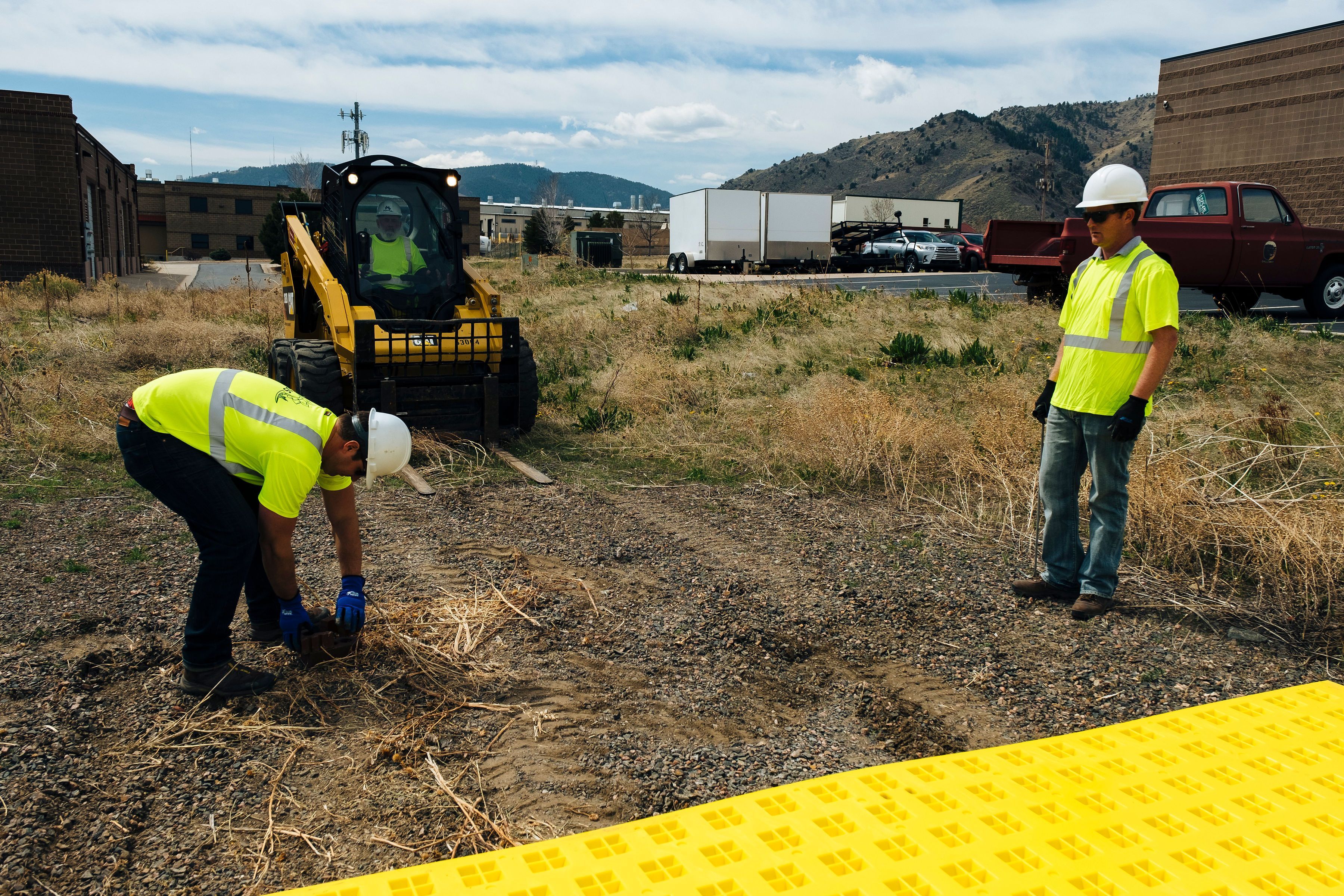

Level the area. Fill any voids and remove any objects such as large rocks, landscaping materials, to avoid abrupt changes in elevation.
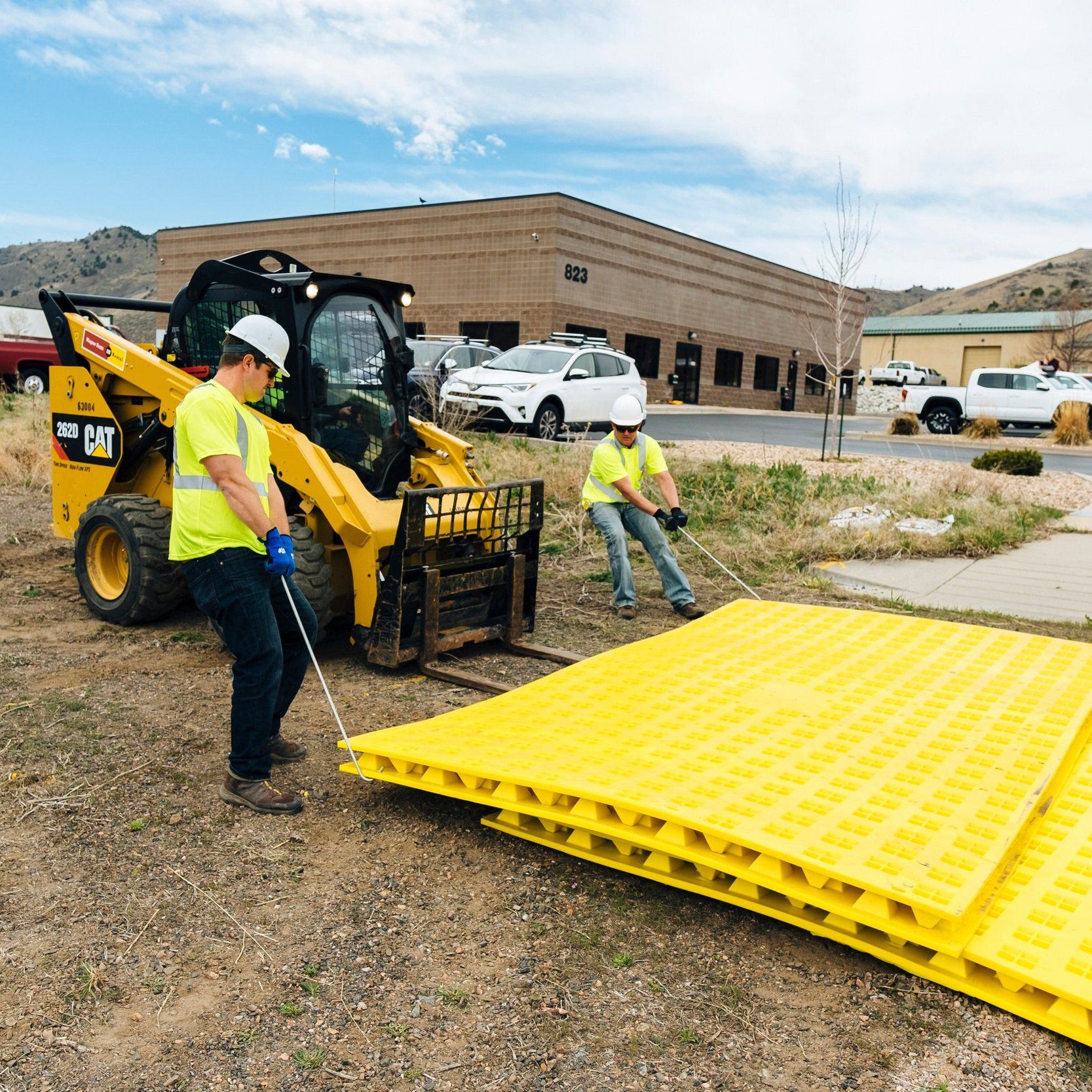

Place the mats in the appropriate configuration using the Mat Moving Tool to pull the mats into place.
Mats can slide over each other so place the nearest mat first.
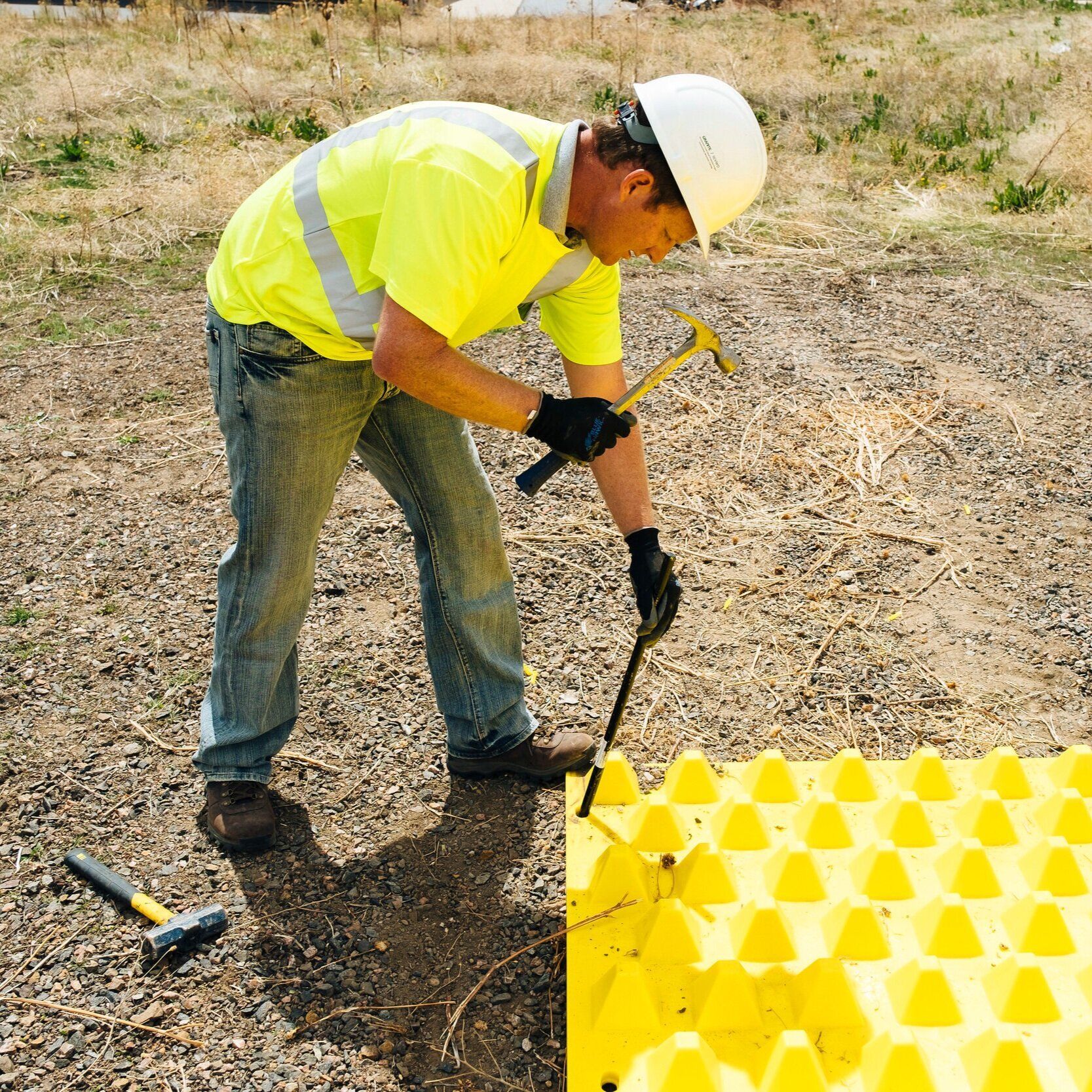

Anchors are always required to secure the mats to the substrate. Use FODS Screw Anchors for installing on concrete or asphalt, and FODS Round Head Stake Anchors for dirt and soft substrates.
Optional hardware kits are available to connect mats together.
Before You Begin
Planning Considerations
- Confirm your SWPPP Requirements.
Select the layout, install, and maintain the FODS entrance in accordance with your local SWPPP and stormwater permit requirements (e.g., EPA CGP/NPDES, state/local manuals). - Call 811 for locates.
Request utility locates at least 3 business days before installation—especially if you plan to anchor into soil, asphalt, or concrete. Do not anchor above marked utilities. - Choose the right spot.
Install the FODS system at the primary/only egress point, as close to the roadway as is safely possible; avoid low points where water pools and do not direct run-off to streets or inlets. Add inlet protection if a drain is nearby. - Prepare the subgrade.
Clear large rocks, landscaping, abrupt grade changes, or ruts; fill/compact soft spots to create a flat, stable surface. This improves tire contact and safety. - Choose the layout.
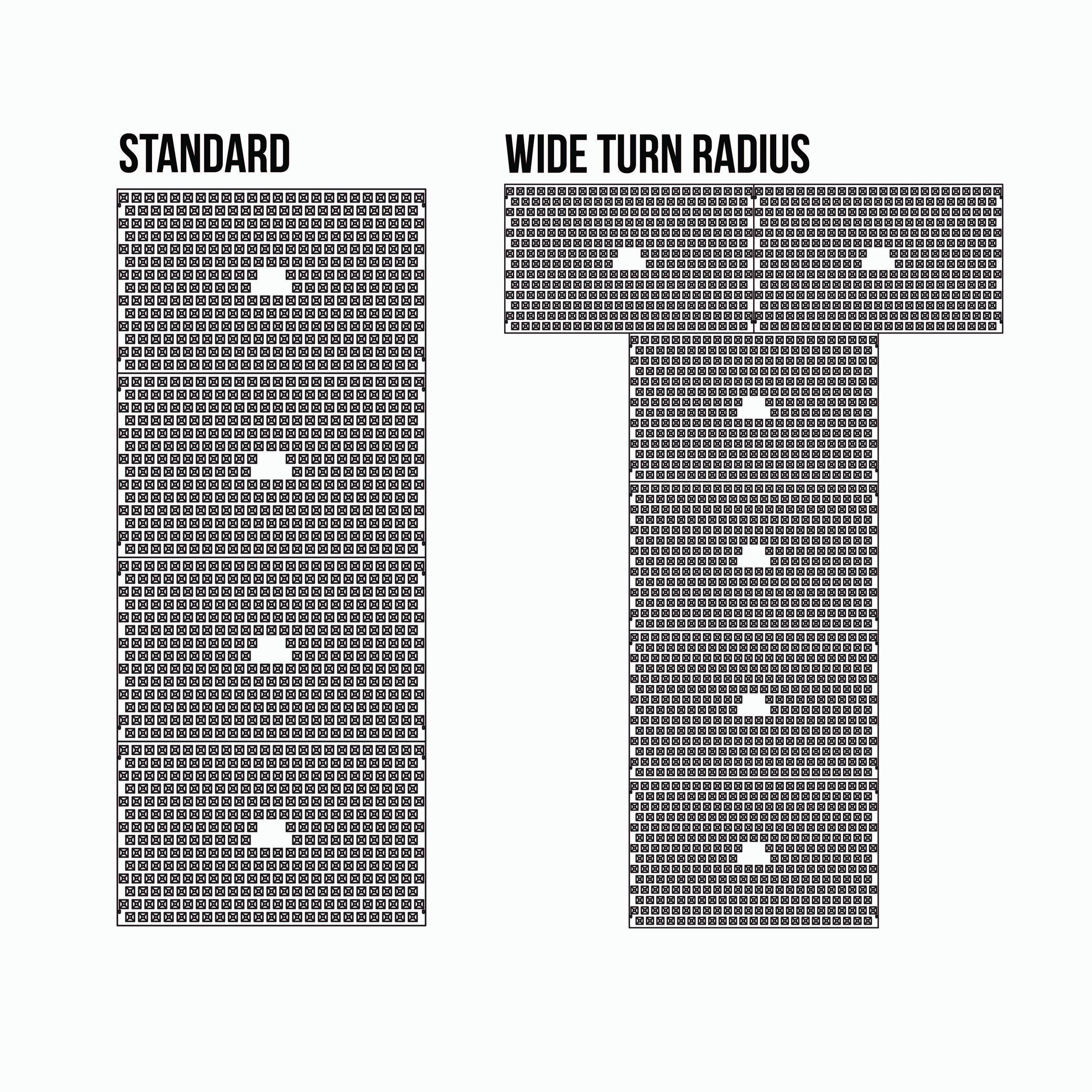
FODS mats are 12 ftwide × 7 ft long and weigh 420 lb each. Plan the number of mats in series to achieve sufficient tire rotations (a common BMP objective), typically via a 1×5 “T” layout (35 ft) or longer where needed. (CDOT recognizes 35 ft of FODS as an alternative to 70 ft of rock.) Use a “T” for increased turn radius.
FODS Installation Resources
Anchoring Hardware Data Sheet
Maintenance Guide
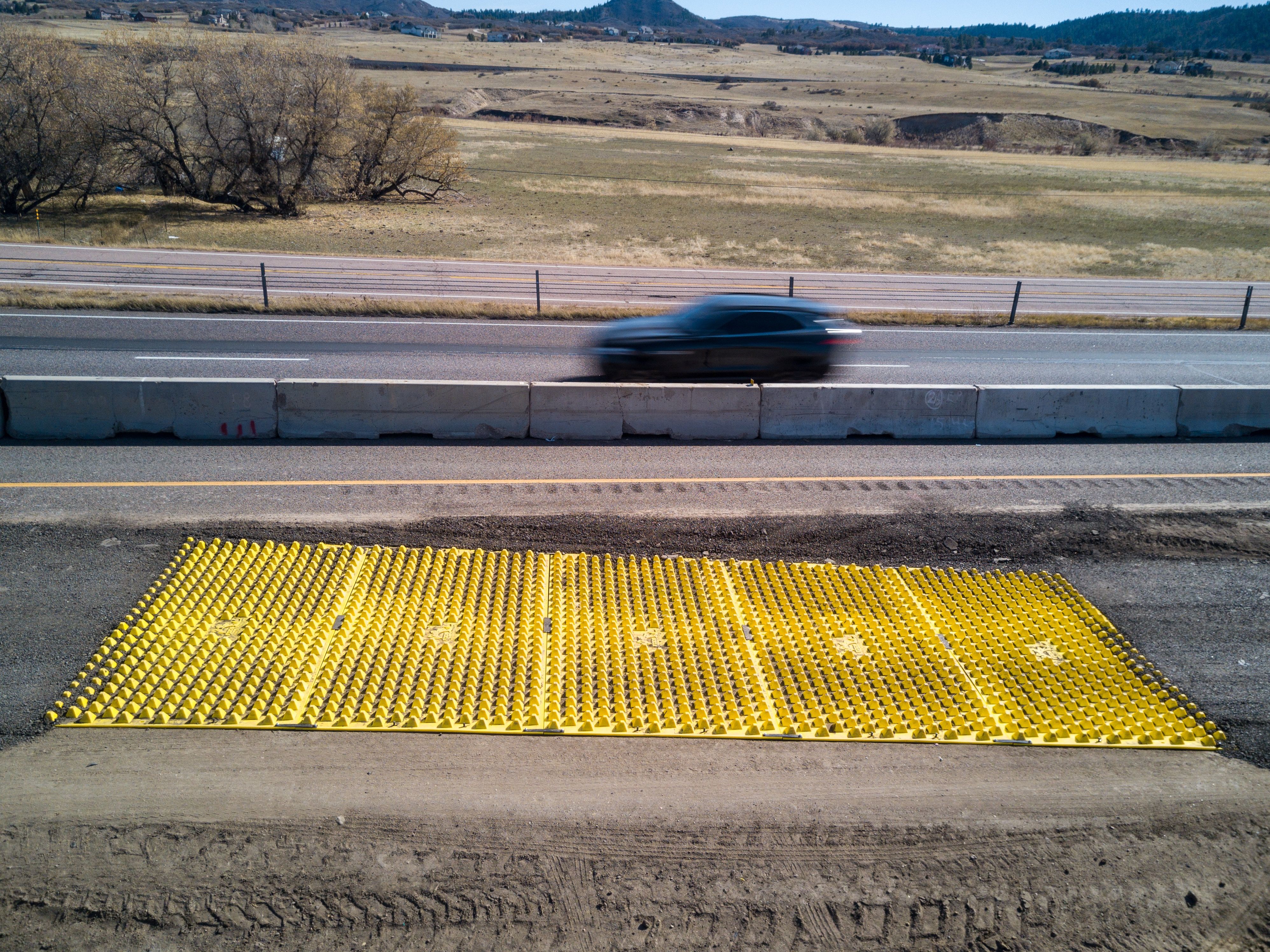

Design Best Practices
- Entrances/exits.
Direct all site traffic across the FODS mats to maximize performance and compliance. - Grade to keep stormwater on-site.
Maintain positive drainage back into the site (not toward the roadway). Add supplemental BMPs (e.g., inlet protection, berms/diversions) as needed by your SWPPP. - Provide adequate length for cleaning.
Many agencies size stabilized exits for 2–3 full tire rotations of the largest vehicles that will use the exit. FODS achieves the same functional performance with shorter length compared to rock entrances due to the pyramidal tread-deforming surface. This results in agencies adjusting recommendations to a shorter distance. For Example: CDOT spec includes 35 ft FODS or 70 ft of rock.
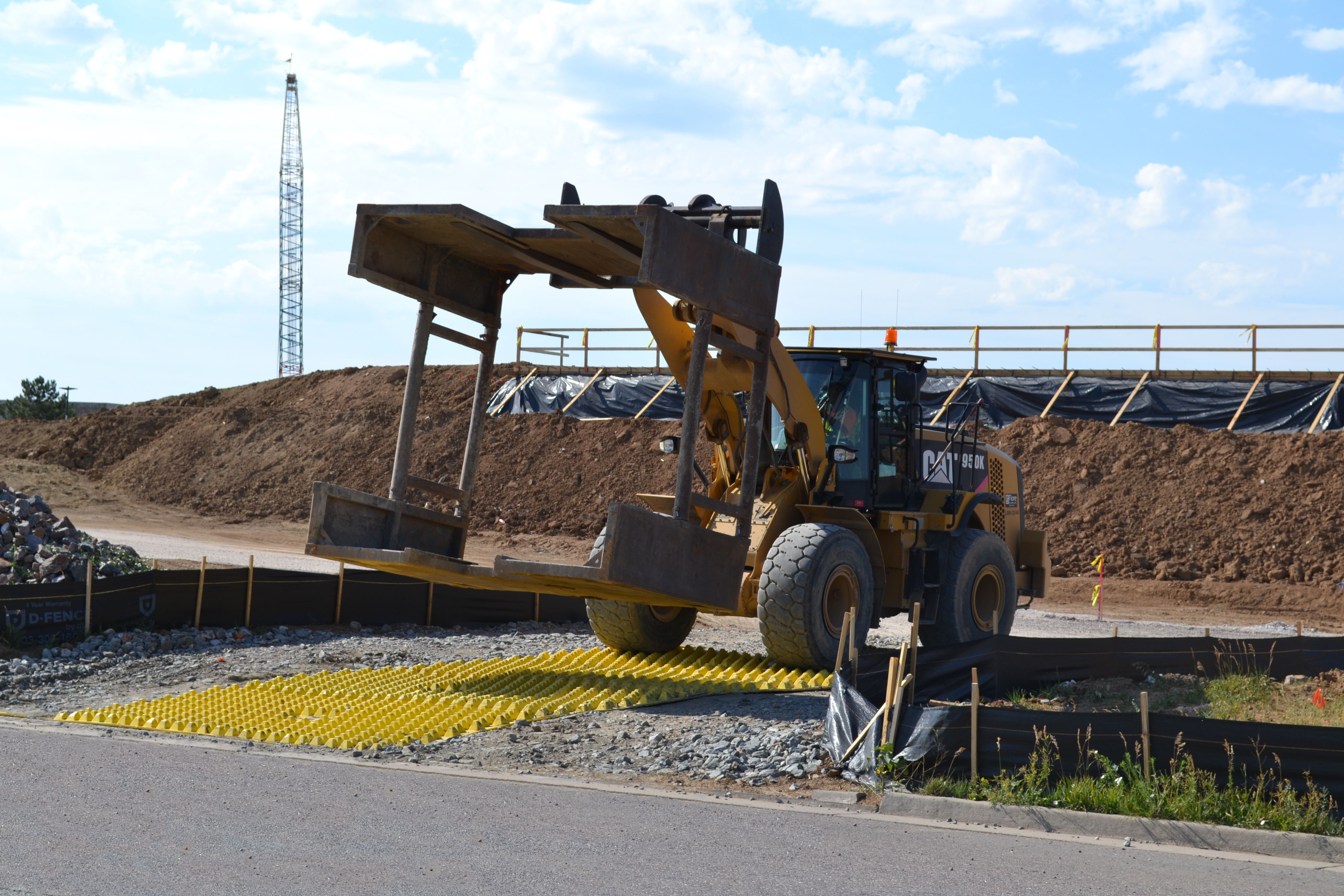

Operations, Inspection & Maintenance
- Daily housekeeping
Inspect nearby paved roads daily; sweep or vacuum to remove any tracked sediment. Increase frequency during wet weather or heavy traffic. - Mat cleaning
Remove accumulated sediment from between pyramids when buildup approaches 2.5 inches (or as specified in your plan). Use a street sweeper, skid/broom, or FODS shovel to remove sediment. Do not wash sediment into inlets. - Storm event inspections
Inspect before forecasted rain, daily during extended rain, and after each event; ensure that mats are clear of debris and properly anchored.

